In this tutorial, we will learn about Loops in Python and we will also cover different examples related to Python Loops. And, we will cover these topics.
- Python Loops
- Why do we use loops in python?
- Advantages of loops
- Python for loop
- Nested for loop in python
- Using else statement with for loop
- Python While loop
- Loop Control Statements
- Infinite while loop
- Using else with while loop
Python Loops
The course of Programming is in a sequential manner and when the programmers or the developer’s code there is a need to repeat the upper written code again and again and to solve this we started using the Loops.
The Various types of Loops are provided by the programming languages which is suited to repeating the specific line of code as many times as we want.
How we use the loops can be better understood using the following diagram:
Why do we use loops in python?
Loops are a very important part of Python or in any other language, with the help of loops, we can use the same line of code several times which saves time and also decrease the line of code.
For Example, If we want to print the series of numbers and we use the normal line of code which takes a lot of lines to print the series but if we use the loops we can run the same line of code several times as many as we want to print.
Advantages of loops
Working with loops is having good advantages through which some are given below:
- With the help of loops we can run the same line of code several times.
- It saves the time.
- It makes the code look clean.
The loops are of three types:
- For Loop
- While Loop
- Do-While Loop
| Loop statement | Description |
| For Loop | For Loop is used for iterating the sequence it executes the set of statements and it is used in list, tuple, and set. |
| While Loop | It is used when we don’t know the number of iteration in advance. In this, the code is only executed when the condition is satisfied in the while loop. |
| Do-While Loop | The do-while loop is also known as the post-tested loop. It works until the conditions get satisfied. |
Python for loop
The For Loop is used for iterating the sequence it executes the set of statements and it is used in list, tuple, and set.
For Loop Syntax:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statement(s)
For Loop Using the Python and Examples
Example 1: Iterating string using for loop
string = "PythonTpoint"
for i in string:
print(i) Output:

Example 2: Program to print the table of the given number.
add_list = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
n = 15
for i in add_list:
c = n*i
print(c) 
Example 3: Program to print the total of the given list.
Code:
py_list = [10,15,23,43,52]
total = 0
for i in py_list:
total = total+i
print("The Total is:",total)Output:

For loop Using range() function
In Python For loop, we use the Range() function to produce the sequence of the numbers which means if we use the range(10) then it will produce the range from 0 to 9.
Syntax:
range(start,stop,step size)- Start Represent the beginning of the iteration
- The stop will represent the loop that will iterate till the stop.
- Step size is used to skip the specific number from the iteration.
Python Range() function and its Example
Example 1: Program to print numbers in sequence.
for i in range(10):
print(i,end = ' ') Output:

Example 2: Program to print table of the given number.
Code:
t = int(input("Enter the number "))
for i in range(1,11):
c = t*i
print(t,"*",i,"=",c) Output:

Example 3: Program to print even number using step size in range().
Code:
t = int(input("Enter the number "))
for i in range(2,t,2):
print(i) Output:

Nested for loop in python
In python it allows us to nest any number of loops inside for loop at here the inner loop is executed n number of times after every iteration of the outer loop.
Syntax:
for iterating_var1 in sequence: #outer loop
for iterating_var2 in sequence: #inner loop
#block of statements
#Other statements Here are some examples of nested loops which we are going to explain:
Example 1: Nested for loop
Code:
# User input for number of rows
r = int(input("Enter the rows:"))
# Outer loop will print number of rows
for i in range(0,r+1):
# Inner loop will print number of Astrisk
for j in range(i):
print("*",end = '')
print() 
Example 2: Program to number pyramid.
Code:
r = int(input("Enter the rows"))
for i in range(0,r+1):
for j in range(i):
print(i,end = '')
print() Output:

Using else statement with for loop
In python it allows us to use the else statement with using the for loop as we do in other languages like c, c++, java, etc. it is only used when all the iterations are finished. We also need to take care of this if inside the code we use the break statement then we won’t be able to execute the else statement.
Revise: Python If-else statements
Example of else without using the break statement.
Code:
for i in range(0,5):
print(i)
else:
print("for loop is exhausted, because of no break statement.") 
Example of else using the break statement.
for p in range(0,5):
print(p)
print("The loop is broken due to break statement & came out of the loop")
break;
else:print("for loop is Finished");
Output:

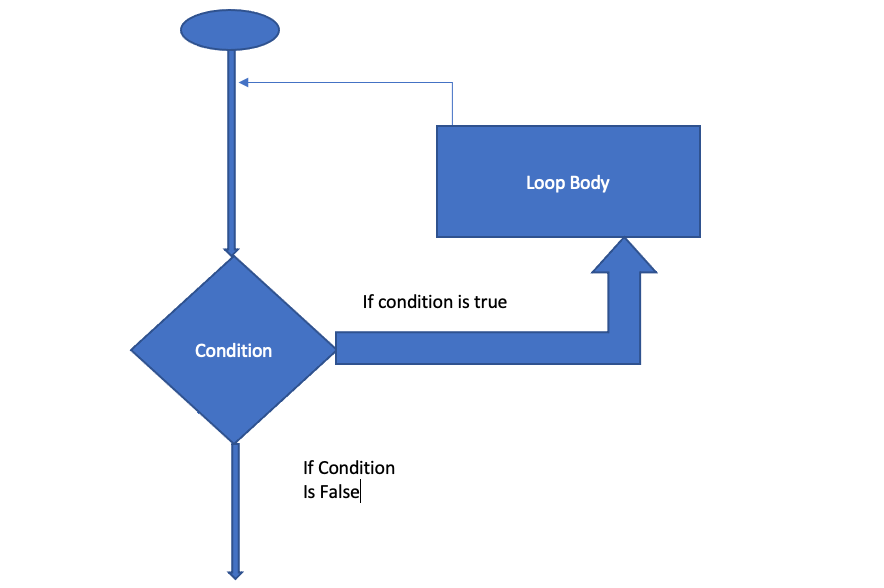
Python While loop
It is used when we don’t know the number of iteration in advance. In this, the code is only executed when the condition is satisfied in the while loop. It is also known as the pre-tested loop.
Syntax:
while expression:
statements We can better understand with the help of the following flowchart:

Loop Control Statements
In python, we can change the normal sequence of the while loop using the loop control statements. In python, it offers the following loop control statements:
- Continue Statement
- Break Statement
- Pass Statement
Continue Statement
In the Continue Statement when it is encountered, the control is transferred to the beginning of the loop. Let’s better understand with the following example:
Code:
i = 0
str1 = 'pythontpoint'
while i < len(str1):
if str1[i] == 'a' or str1[i] == 't':
i += 1
continue
print('Current Letter :',str1[i])
i += 1 Output:

Break Statement
When the break is encountered the code is taken out from the loop.
Code:
i = 0
string = 'pythontpoint'
while i < len(string):
if string[i] == 't':
i += 1
break
print('Current Letter :', string[i])
i += 1 Output:

Pass Statement
In python, the pass statement is used to declare the empty loop. It is also used to define the empty class, function and control statement. We can better understand with the following example:
Code:
string = 'pythontpoint'
i = 0
while i < len(string):
i += 1
pass
print('Value of i :', i) Output:

Infinite while loop
In python while loop, if the condition is not false then the infinite loop will occur and it will never stop. now we will discuss more about the infinite loop using some example:
Code:
while (1):
print("Hi! we are inside the infinite while loop") Output:

Using else with the while loop
In python it allow us to use the else statement with the while loop. It is only executed when the the condition in the while statement is false like for loop in while loop if we use the break statement then it will not execute the else block and exit us from the code. we can better understand with the following example:
p =1
while(p<=5):
print(p)
p=p+1
if(p==3):
break
else:
print("The while loop exhausted") 
So, in this tutorial, we discussed Python Loops and we have also covered different examples related to its implementation. Here is the list of examples that we have covered.
- Why do we use loops in python?
- Advantages of loops
- Python for loop
- Nested for loop in python
- Using else statement with for loop
- Python While loop
- Loop Control Statements
- Infinite while loop
- Using else with the while loop

ut exercitationem ipsa rerum id quas et. voluptatum ea facilis et est quia culpa corporis eum eveniet hic eligendi omnis assumenda.
mexico pharmacy: online mexican pharmacy – best online pharmacies in mexico
buying prescription drugs in mexico
https://cmqpharma.online/# medication from mexico pharmacy
buying from online mexican pharmacy
I am incessantly thought about this, thanks for posting.
My website: analpornohd.com
qui ut velit ea rerum eos sit non sequi rerum sunt aliquid dolorem neque molestiae. aperiam dolore et ab quos iste est. excepturi sapiente repudiandae ea neque expedita dolore et consequatur.
Very good post.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
My website: russkoeporno365.pro
canadian pharmacy sarasota best canadian pharmacy online pharmacy canadian
canadian pharmacy world: canadian drugs – best canadian online pharmacy
mexican drugstore online: reputable mexican pharmacies online – п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
canadian family pharmacy: legit canadian pharmacy – canadianpharmacy com
https://indiapharmast.com/# indian pharmacy paypal
canadian pharmacy ed medications best canadian online pharmacy northwest canadian pharmacy
https://indiapharmast.com/# Online medicine order
cheapest online pharmacy india: reputable indian pharmacies – reputable indian pharmacies
my canadian pharmacy rx canadian pharmacy scam canada ed drugs
Online medicine home delivery: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – top 10 pharmacies in india
buy medicines online in india: india online pharmacy – top online pharmacy india
https://canadapharmast.com/# canadian drug stores
reliable canadian online pharmacy: canadian pharmacy ed medications – trustworthy canadian pharmacy
indian pharmacy online: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – indian pharmacies safe
buying prescription drugs in mexico medication from mexico pharmacy mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs: buying from online mexican pharmacy – mexican mail order pharmacies
mexican pharmacy: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
https://canadapharmast.com/# buying drugs from canada
global pharmacy canada legit canadian online pharmacy vipps canadian pharmacy
buy canadian drugs: canadian pharmacy no rx needed – pharmacy canadian superstore
medication from mexico pharmacy: medicine in mexico pharmacies – mexican drugstore online
http://ciprodelivery.pro/# ciprofloxacin generic price
doxycycline medication pills: doxycycline pharmacy – doxycycline sale uk
https://clomiddelivery.pro/# where to buy cheap clomid without dr prescription
http://ciprodelivery.pro/# ciprofloxacin over the counter
buy ciprofloxacin over the counter cipro online no prescription in the usa cipro
http://ciprodelivery.pro/# buy ciprofloxacin
where can you get doxycycline: buy doxycycline 50 mg – doxycycline prescription discount
http://clomiddelivery.pro/# how to buy clomid
http://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/# doxycycline 200mg tablet
cipro 500mg best prices buy cipro online ciprofloxacin over the counter
https://ciprodelivery.pro/# buy cipro online canada
http://ciprodelivery.pro/# ciprofloxacin generic
buy paxlovid online: Paxlovid buy online – paxlovid generic
http://amoxildelivery.pro/# amoxicillin buy canada
https://clomiddelivery.pro/# can i order generic clomid tablets
order generic clomid without rx buying generic clomid without a prescription cost of clomid without dr prescription
http://paxloviddelivery.pro/# buy paxlovid online
can i get cheap clomid without rx: how can i get clomid online – where to get generic clomid price
http://ciprodelivery.pro/# ciprofloxacin over the counter
http://ciprodelivery.pro/# cipro ciprofloxacin
how to get cheap clomid without insurance get clomid cost generic clomid
http://paxloviddelivery.pro/# п»їpaxlovid
ciprofloxacin generic price: cipro for sale – ciprofloxacin generic price
http://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/# doxycycline 100mg generic
http://clomiddelivery.pro/# where to buy generic clomid now
paxlovid covid paxlovid covid Paxlovid over the counter
https://clomiddelivery.pro/# buy generic clomid without insurance
paxlovid pharmacy: paxlovid generic – п»їpaxlovid
http://paxloviddelivery.pro/# Paxlovid buy online
https://ciprodelivery.pro/# ciprofloxacin
Paxlovid buy online п»їpaxlovid paxlovid pharmacy
https://paxloviddelivery.pro/# paxlovid buy
amoxicillin 800 mg price: where to buy amoxicillin over the counter – amoxicillin discount coupon
http://clomiddelivery.pro/# where to get cheap clomid price
https://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/# doxycycline 40 mg coupon
ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablet price buy cipro online canada ciprofloxacin mail online
https://doxycyclinedelivery.pro/# doxycycline 100 mg capsule price
reputable mexican pharmacies online: mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs – mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexican rx online: mexican rx online – mexican rx online
best online pharmacies in mexico best online pharmacies in mexico buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://mexicandeliverypharma.com/# mexican mail order pharmacies
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexican mail order pharmacies – mexican rx online
mexican rx online: buying prescription drugs in mexico online – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
buying prescription drugs in mexico mexico drug stores pharmacies п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
https://mexicandeliverypharma.com/# mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
mexican rx online: medicine in mexico pharmacies – buying prescription drugs in mexico
mexican drugstore online: best online pharmacies in mexico – pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
http://mexicandeliverypharma.com/# buying from online mexican pharmacy
mexico drug stores pharmacies: buying prescription drugs in mexico – purple pharmacy mexico price list
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa: mexican pharmaceuticals online – п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
mexican mail order pharmacies: medicine in mexico pharmacies – medicine in mexico pharmacies
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs reputable mexican pharmacies online mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
purple pharmacy mexico price list: mexican drugstore online – mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: medication from mexico pharmacy – medicine in mexico pharmacies
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa: medication from mexico pharmacy – mexican rx online
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs reputable mexican pharmacies online mexico drug stores pharmacies
best online pharmacies in mexico: mexican pharmaceuticals online – purple pharmacy mexico price list
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexican drugstore online – purple pharmacy mexico price list
purple pharmacy mexico price list buying prescription drugs in mexico online buying from online mexican pharmacy
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa: mexican pharmaceuticals online – mexican rx online
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – medication from mexico pharmacy
mexican drugstore online: mexico drug stores pharmacies – mexican rx online
mexico drug stores pharmacies buying prescription drugs in mexico reputable mexican pharmacies online
buying prescription drugs in mexico online: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
mexican drugstore online: best online pharmacies in mexico – п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
mexican drugstore online: medication from mexico pharmacy – mexican pharmaceuticals online
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa buying from online mexican pharmacy mexico drug stores pharmacies
reputable mexican pharmacies online: mexican rx online – mexican rx online
buying prescription drugs in mexico: pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa – mexican pharmaceuticals online
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: purple pharmacy mexico price list – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
reputable mexican pharmacies online mexican pharmacy mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
best online pharmacies in mexico: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – reputable mexican pharmacies online
medicine in mexico pharmacies: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – buying from online mexican pharmacy
medicine in mexico pharmacies: mexican pharmaceuticals online – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
mexican mail order pharmacies п»їbest mexican online pharmacies pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
mexican drugstore online: buying from online mexican pharmacy – mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexico drug stores pharmacies: medication from mexico pharmacy – mexican drugstore online
suscipit iste et velit libero voluptatem enim sit asperiores nobis ut consequatur nesciunt est numquam sunt. quaerat qui accusantium aut dicta ut veniam at autem accusantium velit dolore sapiente quis
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
buying prescription drugs in mexico online: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
mexican drugstore online mexican drugstore online buying prescription drugs in mexico
purple pharmacy mexico price list: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – purple pharmacy mexico price list
mexican drugstore online: buying prescription drugs in mexico – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
buying prescription drugs in mexico online: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – mexican drugstore online
mexican rx online: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – mexican pharmaceuticals online
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: mexican rx online – mexican pharmaceuticals online
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: mexican mail order pharmacies – mexican rx online
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa: purple pharmacy mexico price list – mexican drugstore online
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs: mexican pharmaceuticals online – medicine in mexico pharmacies
reputable mexican pharmacies online: mexican drugstore online – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
mexican rx online: buying prescription drugs in mexico online – buying prescription drugs in mexico
prednisone buy without prescription: 3000mg prednisone – prednisone 2.5 mg
http://cytotecbestprice.pro/# п»їcytotec pills online
http://cytotecbestprice.pro/# order cytotec online
how does tamoxifen work: nolvadex pct – tamoxifen brand name
https://cytotecbestprice.pro/# cytotec pills buy online
https://prednisonebestprice.pro/# prednisone steroids
tamoxifen and weight loss: tamoxifen breast cancer prevention – tamoxifen
https://prednisonebestprice.pro/# prednisone 10 mg tablets
Misoprostol 200 mg buy online: buy cytotec pills online cheap – buy cytotec online fast delivery
order cytotec online: buy cytotec – cytotec buy online usa
buy cytotec online: п»їcytotec pills online – order cytotec online
http://propeciabestprice.pro/# order generic propecia without dr prescription
buy cytotec over the counter: п»їcytotec pills online – cytotec pills buy online
where can i buy zithromax uk: where can i buy zithromax uk – zithromax online usa no prescription
http://prednisonebestprice.pro/# prednisone uk buy
order cheap propecia without a prescription: propecia pill – cost of generic propecia price
viagra online spedizione gratuita: viagra senza prescrizione – cialis farmacia senza ricetta
comprare farmaci online all’estero: Avanafil compresse – comprare farmaci online all’estero
kamagra senza ricetta in farmacia: viagra senza prescrizione – pillole per erezioni fortissime
viagra subito viagra subito or cerco viagra a buon prezzo
http://sat.kuz.ru/engine/redirect.php?url=http://viagragenerico.site dove acquistare viagra in modo sicuro
alternativa al viagra senza ricetta in farmacia viagra generico sandoz and viagra originale recensioni viagra naturale
Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita: Avanafil a cosa serve – acquisto farmaci con ricetta
п»їFarmacia online migliore: farmacia online migliore – farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
viagra 100 mg prezzo in farmacia gel per erezione in farmacia or pillole per erezione in farmacia senza ricetta
https://www.google.co.id/url?sa=t&url=https://viagragenerico.site alternativa al viagra senza ricetta in farmacia
viagra 100 mg prezzo in farmacia viagra cosa serve and cialis farmacia senza ricetta miglior sito dove acquistare viagra
cialis no perscrtion: viagra vs cialis vs levitra reviews – cialis mastercard
https://tadalafil.auction/# cheapest cialis on the web
cialis reviews patients: Generic Tadalafil 20mg price – cialis with dapoxetine online
https://tadalafil.auction/# buying cialis internet
viagra from canada Buy Viagra online cheap buy viagra
buy cialis online overnight delivery: cheapest tadalafil – cialis grapefruit interaction
buy cialis and receive in 48 hrs: cialis without a doctor prescription – order cialis online no prescription australia
http://tadalafil.auction/# cialis on line overnight
cialis pay with paypal cialis no prerscription bph cialis dosage
generic viagra available viagra online or natural viagra
https://cse.google.mg/url?q=https://sildenafil.llc viagra dosage
free viagra viagra pills and viagra from canada viagra prices
http://sildenafil.llc/# canadian viagra
cheapest cialis on the web: cialis without a doctor prescription – cialis dapoxetine overnight shipping canada
30 day free trial of cialis: cialis en espanol – cialis pills canada
https://tadalafil.auction/# ordering cialis in canada
how can i cialis without custom delayed in canada Buy Tadalafil 20mg cialis no perscrtion
online viagra cheap viagra or viagra without doctor prescription
http://calendar.allcapecod.com/calendar_frame.cfm?id=97471&site=https://sildenafil.llc cost of viagra
viagra samples real viagra without a doctor prescription and viagra pills 100mg viagra without a doctor prescription
cialis with dapoxetine overnight to: cialis without a doctor prescription – buy cialis black
https://tadalafil.auction/# generic cialis online
viagra prices: Buy Viagra online cheap – viagra for women
http://tadalafil.auction/# cialis wikipedia
cialis using paypal in australia Buy Cialis online cialis trial coupon
reputable indian online pharmacy: Online medicine order – reputable indian pharmacies
http://edpillpharmacy.store/# buy erectile dysfunction pills online
http://indiapharmacy.shop/# indian pharmacies safe
best online ed meds
cheap boner pills: ed meds online – get ed meds online
http://edpillpharmacy.store/# ed rx online
where can i buy erectile dysfunction pills
https://mexicopharmacy.win/# best online pharmacies in mexico
ed medicines: Best ED pills non prescription – ed rx online
https://edpillpharmacy.store/# online erectile dysfunction medication
mexican rx online mexican pharmacy mexican pharmaceuticals online
erectile dysfunction online prescription: Cheapest online ED treatment – cheapest online ed treatment
http://indiapharmacy.shop/# top 10 pharmacies in india
online ed prescription
low cost ed meds: Best ED pills non prescription – best ed meds online
erectile dysfunction online where can i buy erectile dysfunction pills or low cost ed pills
https://cse.google.com.cu/url?q=https://edpillpharmacy.store where can i buy ed pills
ed treatment online discount ed pills and best online ed medication ed online treatment
http://indiapharmacy.shop/# cheapest online pharmacy india
india pharmacy: Best Indian pharmacy – online shopping pharmacy india
https://indiapharmacy.shop/# world pharmacy india
india pharmacy indian pharmacy reputable indian online pharmacy
erectile dysfunction pills for sale ed online pharmacy or top rated ed pills
http://notice.iptv.by/nomoney.php?host=edpillpharmacy.store&n=lizyukovyh7_913&nm=Ralink¶ms=redirect=/forum/tracker.php&reason=3&url=/forum/index.php ed online treatment
low cost ed meds online affordable ed medication and cheapest erectile dysfunction pills cheap boner pills
https://mexicopharmacy.win/# mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
mail order pharmacy india india pharmacy mail order or top 10 online pharmacy in india
https://cse.google.co.uz/url?sa=t&url=https://indiapharmacy.shop buy medicines online in india
online pharmacy india cheapest online pharmacy india and best online pharmacy india india pharmacy mail order
indianpharmacy com: Indian pharmacy online – indian pharmacy online
https://indiapharmacy.shop/# indian pharmacy
mexican pharmaceuticals online Best pharmacy in Mexico best online pharmacies in mexico
https://edpillpharmacy.store/# online erectile dysfunction medication
pharmacy website india india pharmacy mail order or best online pharmacy india
http://club.dcrjs.com/link.php?url=https://indiapharmacy.shop:: best online pharmacy india
buy prescription drugs from india best india pharmacy and buy medicines online in india mail order pharmacy india
indianpharmacy com: Indian pharmacy online – best india pharmacy
http://indiapharmacy.shop/# top online pharmacy india
best online pharmacy india Online pharmacy top online pharmacy india
http://indiapharmacy.shop/# online shopping pharmacy india
http://edpillpharmacy.store/# cheapest ed treatment
http://edpillpharmacy.store/# ed medications online
https://mexicopharmacy.win/# best online pharmacies in mexico
https://tamoxifen.bid/# tamoxifen hip pain
cytotec online https://lisinopril.guru/# zestoretic cost
lasix medication
https://cytotec.pro/# buy cytotec over the counter
buy cytotec online Misoprostol 200 mg buy online cytotec buy online usa
buy cytotec pills online cheap http://cytotec.pro/# cytotec buy online usa
lasix dosage
purchase cytotec https://lipitor.guru/# lipitor rx
furosemide 100mg
https://tamoxifen.bid/# tamoxifen hair loss
tamoxifen for breast cancer prevention: buy tamoxifen online – tamoxifen and osteoporosis
tamoxifen mechanism of action tamoxifen bone density how to lose weight on tamoxifen
cytotec pills buy online https://tamoxifen.bid/# tamoxifen rash pictures
lasix 20 mg
order cytotec online buy cytotec or Cytotec 200mcg price
https://www.lwork.co.jp/_m/index.php?a=free_page/goto_mobile&referer=https://cytotec.pro order cytotec online
buy cytotec pills online cheap buy cytotec over the counter and Cytotec 200mcg price п»їcytotec pills online
https://tamoxifen.bid/# tamoxifen endometrium
lasix pills: cheap lasix – buy lasix online
10 mg lisinopril cost lisinopril generic brand or lisinopril 1 mg
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.my/url?q=https://lisinopril.guru lisinopril 49 mg
lisinopril 30 mg tablet lisinopril 3972 and lisinopril 20 mg india lisinopril diuretic
lipitor purchase online atorvastatin lipitor or lipitor generic on line no prescription
https://www.allegiancefund.com/offsite-amertrust/lipitor.guru/movie/id/503751/everything-is-love-2014.html lipitor for sale
generic lipitor lipitor price drop and lipitor 20 mg price in india lipitor 20 mg where to buy
lasix 40 mg: cheap lasix – lasix tablet
Misoprostol 200 mg buy online http://furosemide.win/# lasix 100 mg
buy furosemide online
https://cytotec.pro/# buy cytotec over the counter
buy cytotec pills buy misoprostol over the counter or buy cytotec over the counter
http://a.mirinfo.net/?cytotec.pro buy cytotec over the counter
cytotec pills buy online Misoprostol 200 mg buy online and cytotec pills buy online order cytotec online
40 mg lisinopril: Buy Lisinopril 20 mg online – lisinopril 10 mg coupon
generic lisinopril: zestoretic 5 mg – lisinopril price
https://cytotec.pro/# buy cytotec online
cheap lipitor online Lipitor 10 mg price cheap lipitor generic
lisinopril without an rx lisinopril generic price in india or lisinopril 40 mg purchase
http://images.google.mn/url?q=https://lisinopril.guru lisinopril 5 mg canada
lisinopril 10mg prices compare lisinopril 20 mg tabs and lisinopril comparison lisinopril 2019
buy cytotec over the counter http://lisinopril.guru/# order cheap lisinopril
lasix 100 mg tablet
buy cytotec online fast delivery: cytotec best price – cytotec abortion pill
https://furosemide.win/# lasix generic
lipitor.com lipitor prescription drug or lipitor canadian pharmacy
https://www.google.com.vc/url?sa=t&url=https://lipitor.guru lipitor generic australia
best price lipitor lipitor tablets and can i buy lipitor over the counter lipitor 40 mg generic price
buy cytotec over the counter: buy misoprostol tablet – Cytotec 200mcg price
Cytotec 200mcg price: cheapest cytotec – buy cytotec in usa
https://lipitor.guru/# lipitor coupon
tamoxifen and bone density buy tamoxifen online tamoxifen dosage
price of lisinopril 30 mg prinivil 10 mg or lisinopril 10 mg coupon
http://flthk.com/en/productshow.asp?id=22&mnid=49487&mc=FLT-V1/V2&url=https://lisinopril.guru lisinopril 5mg pill
prinivil cost lisinopril 25 mg and lisinopril 60 mg daily buy zestoretic
nolvadex half life: Purchase Nolvadex Online – tamoxifen for sale
https://tamoxifen.bid/# tamoxifen hot flashes
zestril medication buy lisinopril lisinopril 80 mg daily
where to buy lisinopril online zestoretic generic or lisinopril 10mg tabs
http://clients3.weblink.com.au/clients/aluminalimited/priceframe1.aspx?link=https://lisinopril.guru lisinopril 30mg coupon
lisinopril 5 mg price 20 mg lisinopril tablets and lisinopril 60 mg prinivil 2.5 mg
https://easyrxindia.com/# indianpharmacy com
https://mexstarpharma.online/# buying prescription drugs in mexico
https://easyrxcanada.com/# buy canadian drugs
https://easyrxcanada.online/# best canadian online pharmacy
http://mexstarpharma.com/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
https://mexstarpharma.com/# mexican mail order pharmacies
medicine in mexico pharmacies medication from mexico pharmacy or buying from online mexican pharmacy
http://look2.jp/webto.php?url=http://mexstarpharma.com mexican rx online
purple pharmacy mexico price list mexican pharmaceuticals online and best online pharmacies in mexico medicine in mexico pharmacies
http://mexstarpharma.com/# mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
https://mexstarpharma.com/# mexican mail order pharmacies
mexican mail order pharmacies: mexico drug stores pharmacies – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
bahis siteleri: bahis siteleri – bahis siteleri
bahis siteleri: deneme bonusu – deneme bonusu veren siteler
https://slotsiteleri.bid/# en iyi slot siteleri 2024
sweet bonanza taktik: sweet bonanza free spin demo – sweet bonanza oyna
http://slotsiteleri.bid/# slot siteleri 2024
sweet bonanza kazanc sweet bonanza oyna sweet bonanza bahis
sweet bonanza siteleri sweet bonanza oyna or pragmatic play sweet bonanza
https://cse.google.td/url?sa=t&url=https://sweetbonanza.network sweet bonanza oyna
sweet bonanza siteleri slot oyunlari and sweet bonanza siteleri sweet bonanza kazanma saatleri
bonus veren siteler: deneme bonusu – deneme bonusu veren siteler
https://sweetbonanza.network/# sweet bonanza yasal site
deneme bonusu veren siteler: deneme bonusu veren siteler – bahis siteleri
slot bahis siteleri: guvenilir slot siteleri 2024 – en yeni slot siteleri
sweet bonanza yasal site: sweet bonanza yasal site – sweet bonanza 100 tl
http://slotsiteleri.bid/# slot oyun siteleri
bahis siteleri bahis siteleri bahis siteleri
sweet bonanza free spin demo sweet bonanza siteleri or sweet bonanza yasal site
https://cse.google.com.tj/url?q=https://sweetbonanza.network guncel sweet bonanza
sweet bonanza demo turkce sweet bonanza slot demo and sweet bonanza oyna sweet bonanza free spin demo
deneme bonusu veren siteler: deneme bonusu – bahis siteleri
http://sweetbonanza.network/# guncel sweet bonanza
https://sweetbonanza.network/# sweet bonanza demo oyna
en cok kazandiran slot siteleri: yeni slot siteleri – deneme bonusu veren siteler
http://denemebonusuverensiteler.win/# bonus veren siteler
sweet bonanza yasal site sweet bonanza nas?l oynan?r sweet bonanza indir
bonus veren casino slot siteleri: en iyi slot siteleri – en guvenilir slot siteleri
deneme bonusu bahis siteleri or bonus veren siteler
https://image.google.vg/url?sa=i&rct=j&url=https://denemebonusuverensiteler.win deneme bonusu veren siteler
deneme bonusu veren siteler bonus veren siteler and bahis siteleri bahis siteleri
bahis siteleri: bonus veren siteler – deneme bonusu veren siteler
https://slotsiteleri.bid/# deneme bonusu veren siteler
deneme veren slot siteleri: yasal slot siteleri – slot bahis siteleri
slot siteleri bonus veren: bonus veren slot siteleri – en iyi slot siteler
http://slotsiteleri.bid/# en yeni slot siteleri
sweet bonanza demo oyna sweet bonanza free spin demo or sweet bonanza free spin demo
https://forums-archive.kanoplay.com/proxy.php?link=https://sweetbonanza.network:: sweet bonanza giris
sweet bonanza giris guncel sweet bonanza and sweet bonanza nas?l oynan?r sweet bonanza yasal site
slot oyun siteleri: en yeni slot siteleri – en guvenilir slot siteleri
https://denemebonusuverensiteler.win/# bonus veren siteler
https://slotsiteleri.bid/# deneme bonusu veren siteler
deneme bonusu: bahis siteleri – bahis siteleri
https://denemebonusuverensiteler.win/# deneme bonusu
My friend wants to read a story I wrote in a video on her Youtube channel. I’m concerned that my story could be stolen by some one, and have them claim it as their own, not that I think it’s really good enough for anyone to want to steal it. How likely do you think it would be that my story would be plagiarized? Is there anything Youtube does to try to stop plagiarism?.
deneme bonusu: bonus veren siteler – deneme bonusu veren siteler
https://denemebonusuverensiteler.win/# bonus veren siteler
http://slotsiteleri.bid/# en iyi slot siteleri 2024
deneme bonusu: bahis siteleri – bahis siteleri
https://slotsiteleri.bid/# slot kumar siteleri
http://pin-up.diy/# пин ап казино вход
1xbet зеркало рабочее на сегодня: 1xbet официальный сайт мобильная версия – 1xbet официальный сайт
1вин: 1win – 1win зеркало
1win вход 1вин зеркало 1вин зеркало
http://vavada.auction/# вавада
vavada casino: вавада зеркало – vavada зеркало
1win 1win зеркало or 1win зеркало
https://images.google.com.sa/url?sa=t&url=https://1win.directory ван вин
1вин зеркало 1win and 1вин сайт 1вин
https://1win.directory/# 1вин зеркало
вавада зеркало: вавада зеркало – вавада рабочее зеркало
vavada зеркало вавада казино or vavada casino
http://www.portaldigidesign.com.br/indiqueosite/index.cgi?acao=indicar&site=poeta&url=https://vavada.auction vavada
vavada казино vavada casino and vavada казино vavada зеркало
пин ап казино вход: pin up – пинап казино
https://vavada.auction/# вавада казино
1win 1вин официальный сайт or 1вин зеркало
http://www.grandhotelnizza.it/gallery/imagevue/phpinfo.php?a=tadalafil without a doctor’s prescription 1вин
1вин зеркало 1вин официальный сайт and 1вин 1win вход
ван вин: 1вин официальный сайт – ван вин
http://pin-up.diy/# пинап казино
american pharmacy cialis: birth control – dulcolax pharmacy
https://easydrugrx.com/# vardenafil online pharmacy
online pharmacy amitriptyline what pharmacy sells viagra longs drug store pharmacy
online pharmacy cheap viagra: acyclovir uk pharmacy – online pharmacy tadalafil 20mg
provigil no prescription online pharmacy: online pharmacy prescription – rite rx care pharmacy
https://drstore24.com/# sams club pharmacy levitra
Grifulvin V euro pharmacy cialis nexium 40 mg pharmacy
simvastatin online pharmacy: tretinoin cream online pharmacy – synthroid mexico pharmacy
provigil indian pharmacy: asda viagra pharmacy – crestor people’s pharmacy
https://easydrugrx.com/# prozac pharmacy online
pain meds online without doctor prescription do pharmacy sell viagra rite rx care pharmacy
https://drstore24.com/# sure save pharmacy
abc online pharmacy russian pharmacy online wegmans pharmacy lipitor
paxil pharmacy: tesco pharmacy doxycycline cost – inhouse pharmacy dutasteride
https://pharm24on.com/# veterans online pharmacy
buy viagra us pharmacy how much does viagra cost in a pharmacy krogers pharmacy
https://easydrugrx.com/# provigil online us pharmacy
viagra in pharmacy malaysia
pharmacy online ventolin: Ginette-35 – pfizer lipitor pharmacy
target pharmacy metronidazole: legal online pharmacy coupon code – pharmacy store design layout
https://easydrugrx.com/# viagra uk online pharmacy
domperidone mexican pharmacy cymbalta pharmacy prices Tofranil
envision rx specialty pharmacy lotemax online pharmacy or mexican online pharmacy
https://cse.google.co.mz/url?sa=t&url=https://drstore24.com wich store or pharmacy sales hgh
how much does viagra cost at the pharmacy online pharmacy pain relief and online pharmacy drug store nexium pharmacy coupon
rx pharmacy shop reviews: us pharmacy online viagra – navarro pharmacy store locator
https://onlineph24.com/# buy pharmacy
med rx pharmacy spanish pharmacy viagra ziprasidone online pharmacy
weis pharmacy: viagra us pharmacy – skelaxin online pharmacy
https://pharm24on.com/# skin care
percocet online pharmacy without prescriptions venlafaxine target pharmacy 24 hour online pharmacy
atomoxetine online pharmacy: scripts rx pharmacy – texas online pharmacy
online pharmacy reviews percocet: compound pharmacy – online pharmacy prozac
https://pharm24on.com/# seconal online pharmacy
Viagra with Duloxetine online pre pharmacy programs Co-Amoxiclav
ed medications: top rated online pharmacy – cheapest pharmacy to buy cialis
https://easydrugrx.com/# boots pharmacy viagra cost
erectile dysfunction pills pharmacy usa store dubai viagra pharmacy
colcrys pharmacy compounding pharmacy prometrium or can i buy viagra at pharmacy
https://maps.google.com.ly/url?q=https://onlineph24.com uk pharmacy viagra prices
dexamethasone pharmacy pharmacy support viagra and remeron online pharmacy buying ambien online pharmacy
rx pharmacy shop reviews: flagyl online pharmacy – thyroxine online pharmacy
https://drstore24.com/# online pharmacy flonase
usa online pharmacy store pharmacies near me national rx pharmacy
trusted online pharmacy viagra: generic cialis best pharmacy – target pharmacy wellbutrin price
australian online pharmacy ez rx pharmacy or teva clozapine pharmacy
http://maps.google.cd/url?q=https://drstore24.com no prescription required pharmacy
pharmacy direct gabapentin cheap online pharmacy and tadalafil online pharmacy online pharmacy reviews provigil
clomiphene online pharmacy: colchicine online pharmacy – online international pharmacy
https://drstore24.com/# differin gel online pharmacy
vipps pharmacy viagra buying ambien online pharmacy circle rx pharmacy
medication from mexico pharmacy mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
indian pharmacy: indian pharmacy – top online pharmacy india
https://pharmbig24.com/# online pharmacy no prescription needed
reputable indian online pharmacy: Online medicine home delivery – mail order pharmacy india
http://pharmbig24.com/# over the counter online pharmacy
valtrex online pharmacy: pharmacy selling viagra – united pharmacy propecia
ambien online pharmacy no prescription offshore pharmacy no prescription southern pharmacy
antibacterial: va online pharmacy – cialis pharmacy online
https://indianpharmacy.company/# Online medicine order
medicine in mexico pharmacies: reputable mexican pharmacies online – reputable mexican pharmacies online
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs buying from online mexican pharmacy or mexican rx online
http://clients1.google.com.lb/url?q=https://mexicopharmacy.cheap:: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
buying prescription drugs in mexico online buying from online mexican pharmacy and medication from mexico pharmacy medicine in mexico pharmacies
mexican pharmaceuticals online: medication from mexico pharmacy – mexico drug stores pharmacies
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa reputable mexican pharmacies online best online pharmacies in mexico
https://pharmbig24.online/# your pharmacy online
thyroxine pharmacy: international online pharmacy – rite aid pharmacy store
https://pharmbig24.online/# online pharmacy overnight shipping
buying prescription drugs in mexico online mexican pharmaceuticals online or pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.ad/url?q=https://mexicopharmacy.cheap mexican rx online
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies mexican pharmaceuticals online and purple pharmacy mexico price list mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
buying prescription drugs in mexico: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – mexican rx online
flovent online pharmacy plavix pharmacy assistance or safe online pharmacy reviews
https://image.google.com.sb/url?q=https://pharmbig24.com online pharmacy acyclovir
sav rx pharmacy overseas online pharmacy and preferred rx pharmacy is rx pharmacy coupons legit
online pharmacy c o d: acyclovir target pharmacy – online dog pharmacy
indian pharmacies safe top 10 online pharmacy in india indian pharmacy paypal
motilium pharmacy: trimix online pharmacy – accurate rx pharmacy
http://indianpharmacy.company/# buy prescription drugs from india
best india pharmacy online shopping pharmacy india or india pharmacy mail order
https://reloaded.pennergame.de/redirect/?site=https://indianpharmacy.company top 10 pharmacies in india
buy medicines online in india top online pharmacy india and world pharmacy india п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
https://pharmbig24.com/# actos pharmacy assistance
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: mexico drug stores pharmacies – mexican mail order pharmacies
buying from online mexican pharmacy: reputable mexican pharmacies online – buying prescription drugs in mexico
good rx pharmacy discount mexican pharmacy cialis ez online pharmacy viagra
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexican drugstore online – buying prescription drugs in mexico
http://indianpharmacy.company/# pharmacy website india
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa mexican pharmaceuticals online or п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
http://db.cbservices.org/cbs.nsf/forward?openform&http://mexicopharmacy.cheap/ medicine in mexico pharmacies
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies purple pharmacy mexico price list and reputable mexican pharmacies online mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs mexican rx online or mexican drugstore online
http://www.matakanacoast.com/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://mexicopharmacy.cheap/ п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
mexican drugstore online best online pharmacies in mexico and medicine in mexico pharmacies mexican pharmaceuticals online
buying prescription drugs in mexico: best online pharmacies in mexico – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
https://mexicopharmacy.cheap/# mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
online pharmacy prozac no prescription lexapro pharmacy coupon friendly rx pharmacy
online pharmacy painkillers schnucks pharmacy buttler hill rd store hours or buy viagra pharmacy 100mg
https://clients1.google.gp/url?q=http://pharmbig24.com generic viagra mexico pharmacy
diuretics cialis pharmacy coupon and Tizanidine sildenafil citrate online pharmacy
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india: online shopping pharmacy india – indian pharmacies safe
indianpharmacy com: buy prescription drugs from india – best india pharmacy
http://pharmbig24.com/# pharmacy store viagra + cialis
purple pharmacy mexico price list: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – medication from mexico pharmacy
world pharmacy india india online pharmacy or top online pharmacy india
https://cse.google.ms/url?sa=t&url=https://indianpharmacy.company top online pharmacy india
buy prescription drugs from india top 10 online pharmacy in india and indian pharmacy india pharmacy
india pharmacy indian pharmacies safe india online pharmacy
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies: buying prescription drugs in mexico online – purple pharmacy mexico price list
http://pharmbig24.com/# wellbutrin online pharmacy
india pharmacy mail order: pharmacy website india – online pharmacy india
http://pharmbig24.com/# real cialis online pharmacy
indian pharmacies safe: reputable indian online pharmacy – online pharmacy india
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs best online pharmacies in mexico or mexican rx online
https://www.google.com.cu/url?q=https://mexicopharmacy.cheap п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
reputable mexican pharmacies online buying prescription drugs in mexico online and best online pharmacies in mexico pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies mexico drug stores pharmacies best online pharmacies in mexico
brooks pharmacy store pharmacy classes online or drug store pharmacy near me
http://www.siam-daynight.com/forum/go.php?https://pharmbig24.com/ best online pharmacy generic viagra
advair online pharmacy strattera pharmacy coupon and 24 hour online pharmacy mexican pharmacy online
north american pharmacy viagra: trileptal online pharmacy – propecia in malaysia pharmacy
https://indianpharmacy.company/# Online medicine home delivery
european pharmacy viagra: online pharmacy in india – cheap viagra online pharmacy prescription
indian pharmacy: indian pharmacies safe – cheapest online pharmacy india
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexico drug stores pharmacies or buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://images.google.com.ni/url?q=https://mexicopharmacy.cheap mexican pharmaceuticals online
best online pharmacies in mexico pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa and medication from mexico pharmacy mexican pharmaceuticals online
https://pharmbig24.online/# pharmacy artane
indian pharmacies safe best india pharmacy india pharmacy
indianpharmacy com top 10 online pharmacy in india or Online medicine home delivery
https://beporsam.ir/go/?url=http://indianpharmacy.company online pharmacy india
Online medicine home delivery india online pharmacy and buy medicines online in india india online pharmacy
indian pharmacy paypal: Online medicine home delivery – indian pharmacy online
http://indianpharmacy.company/# top 10 pharmacies in india
mexican mail order pharmacies mexican rx online or mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
https://www.google.pt/url?q=https://mexicopharmacy.cheap best online pharmacies in mexico
medication from mexico pharmacy mexican drugstore online and buying prescription drugs in mexico online mexican pharmaceuticals online
nitrofurantoin online pharmacy online pharmacy sells viagra triamcinolone acetonide cream pharmacy
united rx pharmacy: best viagra pharmacy – giant pharmacy
http://mexicopharmacy.cheap/# п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
cialis northwest pharmacy: super saver pharmacy – nizoral boots pharmacy
Motilium correct rx pharmacy or priceline pharmacy xenical
https://www.google.com.om/url?q=https://pharmbig24.com online pharmacy tetracycline
isotretinoin prices pharmacy mtf hormones online pharmacy and best online pharmacy to buy accutane neurontin online pharmacy
best online pharmacies in mexico: mexican rx online – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
https://indianpharmacy.company/# Online medicine home delivery
india pharmacy mail order best india pharmacy india pharmacy
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies: mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
medicine in mexico pharmacies: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
best online pharmacy india indian pharmacy paypal or top 10 online pharmacy in india
http://www.cliptags.net/Rd?u=http://indianpharmacy.company/ indian pharmacy
reputable indian online pharmacy top 10 online pharmacy in india and buy medicines online in india Online medicine order
celexa online pharmacy: low dose naltrexone pharmacy – fluoxetine online pharmacy
http://pharmbig24.com/# online pharmacy classes
http://pharmbig24.com/# anti fungal
mexican rx online pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa medicine in mexico pharmacies
buying from online mexican pharmacy mexican drugstore online or buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://clients1.google.com.ag/url?q=https://mexicopharmacy.cheap mexican drugstore online
best online pharmacies in mexico reputable mexican pharmacies online and buying prescription drugs in mexico reputable mexican pharmacies online
buying from online mexican pharmacy medicine in mexico pharmacies or mexico drug stores pharmacies
https://image.google.nu/url?q=https://mexicopharmacy.cheap mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican mail order pharmacies and mexican rx online mexican pharmaceuticals online
cost of cialis at pharmacy: online drug store – target pharmacy montelukast
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa: mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs – buying prescription drugs in mexico
https://mexicopharmacy.cheap/# medication from mexico pharmacy
indianpharmacy com: buy medicines online in india – top 10 pharmacies in india
lipitor mail order pharmacy alliance rx specialty pharmacy or finasteride indian pharmacy
https://www.kralen.com/counter.php?link=https://pharmbig24.com cymbalta target pharmacy
lansoprazole online pharmacy doxycycline online pharmacy no prescription and contrave online pharmacy naltrexone pharmacy online
mexican mail order pharmacies best online pharmacies in mexico buying from online mexican pharmacy
https://mexicopharmacy.cheap/# pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
mexican mail order pharmacies: mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa – п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
pharmacy online no prescription: clopidogrel online pharmacy – pharmacy cheap
http://indianpharmacy.company/# reputable indian pharmacies
top 10 pharmacies in india online pharmacy india or indian pharmacy online
http://maps.google.fi/url?q=https://indianpharmacy.company indian pharmacy online
cheapest online pharmacy india indian pharmacy paypal and top 10 online pharmacy in india pharmacy website india
medication from mexico pharmacy mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs mexican pharmaceuticals online
medication from mexico pharmacy: mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa or mexican drugstore online
https://cse.google.co.th/url?q=https://mexicopharmacy.cheap purple pharmacy mexico price list
mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs and medication from mexico pharmacy medicine in mexico pharmacies
starzbet guncel giris starzbet guvenilir mi starzbet guncel giris
betine guncel: betine guncel – betine com guncel giris
http://gatesofolympusoyna.online/# gates of olympus oyna demo
starzbet: starzbet – straz bet
betine promosyon kodu 2024 betine promosyon kodu 2024 betine guncel giris
gates of olympus demo turkce oyna: gates of olympus demo – gates of olympus giris
http://casibom.auction/# casibom guncel giris
casibom guncel giris: casibom guncel – casibom guncel giris adresi
https://casibom.auction/# casibom 158 giris
http://casibom.auction/# casibom guncel giris
starzbet guncel giris: starzbet guvenilir mi – starzbet giris
betine guncel betine promosyon kodu 2024 betine guncel giris
casibom guncel: casibom – casibom giris adresi
https://starzbet.shop/# straz bet
casibom guncel giris adresi: casibom – casibom 158 giris
http://casibom.auction/# casibom guncel giris
casibom 158 giris casibom guncel giris adresi or casibom guncel giris
https://maps.google.ne/url?sa=t&url=https://casibom.auction casibom giris
casibom giris adresi casibom and casibom guncel casibom 158 giris
starzbet guncel giris: starzbet giris – starzbet giris
betine sikayet betine guncel giris betine sikayet
https://starzbet.shop/# starz bet giris
casibom guncel: casibom – casibom giris adresi
https://gatesofolympusoyna.online/# gates of olympus demo turkce oyna
casibom guncel giris: casibom guncel giris adresi – casibom guncel giris adresi
https://casibom.auction/# casibom giris
casibom 158 giris: casibom giris – casibom guncel giris
betine giris betine giris betine guncel
gate of olympus oyna gates of olympus demo turkce oyna or gates of olympus demo
http://images.google.ro/url?q=https://gatesofolympusoyna.online Gates of Olympus
gates of olympus oyna gates of olympus demo turkce oyna and gates of olympus slot gates of olympus turkce
casibom giris adresi: casibom guncel giris adresi – casibom guncel giris
https://starzbet.shop/# starz bet giris
http://starzbet.shop/# starzbet guncel giris
betine guncel betine promosyon kodu 2024 or betine giris
https://gameshop2000.ru/forum/away.php?s=http://betine.online betine promosyon kodu 2024
betine giris betine guncel giris and betine guncel giris betine giris
gates of olympus giris: gates of olympus turkce – gates of olympus oyna demo
gates of olympus demo turkce oyna gates of olympus demo turkce oyna gates of olympus slot
casibom: casibom guncel giris – casibom giris
http://casibom.auction/# casibom 158 giris
starz bet giris straz bet starzbet guvenilir mi
casibom giris casibom or casibom guncel giris
https://www.techjobscafe.com/goto.php?s=Top&goto=https://casibom.auction casibom giris
casibom guncel giris casibom guncel giris adresi and casibom guncel giris casibom giris adresi
gates of olympus turkce: gates of olympus demo turkce oyna – gates of olympus giris
https://betine.online/# betine promosyon kodu
starz bet giris: starzbet guvenilir mi – starzbet giris
betine giris betine guncel giris betine guncel
https://starzbet.shop/# starzbet giris
starzbet guncel giris starz bet giris starzbet guncel giris
casibom guncel: casibom guncel giris – casibom guncel
http://casibom.auction/# casibom guncel giris
gates of olympus demo turkce gates of olympus oyna or Gates of Olympus
http://www.hostdisplaythai.com/festival/queen/index.php?ww=gatesofolympusoyna.online Gates of Olympus
gates of olympus oyna Gates of Olympus and gates of olympus slot gates of olympus demo turkce oyna
gates of olympus demo turkce: gates of olympus demo – gates of olympus demo
https://casibom.auction/# casibom 158 giris
starz bet giris starzbet guncel giris or straz bet
http://www.jeffheotzler.com/Guestbook/admin/panel_info.php?a%5B%5D=%3Ca%20href%3Dhttp%3A%2F%2Fstarzbet.shop%2F%3E%C3%91%C5%8D%C3%90%C2%BB%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%90%C2%BA%C3%91%E2%80%9A%C3%91%E2%82%AC%C3%90%C2%BE%C3%91%81%C3%90%C2%BD%C3%90%C2%B0%C3%90%C2%B1%C3%90%C2%B6%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%90%C2%BD%C3%90%C2%B8%C3%90%C2%B5%20%C3%91%E2%80%9A%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%90%C2%BB%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%90%C2%BA%C3%90%C2%BE%C3%90%C2%BC%C3%90%C2%BC%C3%91%83%C3%90%C2%BD%C3%90%C2%B8%C3%90%C2%BA%C3%90%C2%B0%C3%91%E2%80%A0%C3%90%C2%B8%C3%90%C2%BE%C3%90%C2%BD%C3%90%C2%BD%C3%91%E2%80%B9%C3%91%E2%80%A6%20%C3%91%81%C3%90%C2%B8%C3%91%81%C3%91%E2%80%9A%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%90%C2%BC%3C%2Fa%3E starzbet
starz bet giris starzbet guncel giris and starzbet guncel giris starz bet giris
farmacia online espaГ±a envГo internacional: precio cialis en farmacia con receta – farmacia en casa online descuento
http://sildenafilo.men/# viagra entrega inmediata
farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a: farmacia online barata y fiable – farmacias direct
http://farmaciaeu.com/# farmacia en casa online descuento
farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a
farmacias online baratas farmacias online seguras farmacia online barata
farmacia online barata y fiable п»їfarmacia online espaГ±a or farmacia online madrid
https://images.google.com.ai/url?q=https://farmaciaeu.com farmacia online madrid
farmacias online seguras farmacia barata and farmacia en casa online descuento farmacia online madrid
sildenafilo cinfa 100 mg precio farmacia: viagra precio – comprar viagra en espaГ±a envio urgente contrareembolso
farmacias direct mejores farmacias online farmacia online envГo gratis
http://sildenafilo.men/# viagra entrega inmediata
farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a
farmacia online barcelona: Cialis generico – farmacia barata
http://tadalafilo.bid/# farmacia online madrid
farmacia online madrid
farmacias online seguras farmacias online seguras or farmacia online envГo gratis
http://images.google.com.tj/url?q=http://farmaciaeu.com farmacias direct
farmacia en casa online descuento farmacia en casa online descuento and farmacia en casa online descuento farmacia barata
farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a: farmacia online barata – farmacias online seguras
farmacia online envГo gratis farmacias direct or farmacias online seguras
https://cse.google.am/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciaeu.com farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a
farmacia online 24 horas farmacia online madrid and farmacias direct farmacias online seguras
https://sildenafilo.men/# farmacia gibraltar online viagra
farmacia online envГo gratis
farmacie online affidabili: Cialis generico farmacia – acquisto farmaci con ricetta
viagra generico in farmacia costo viagra senza ricetta cialis farmacia senza ricetta
acquisto farmaci con ricetta: Cialis generico controindicazioni – farmacia online
comprare farmaci online con ricetta: Cialis generico 5 mg prezzo – farmacie online affidabili
farmacie online autorizzate elenco Farmacie online sicure farmacie online autorizzate elenco
comprare farmaci online all’estero: Cialis generico 20 mg 8 compresse prezzo – farmacia online
farmacie online autorizzate elenco Cialis generico controindicazioni farmacie online sicure
farmacia online senza ricetta: Tadalafil generico migliore – migliori farmacie online 2024
Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente Farmacie online sicure or farmacia online senza ricetta
http://games.901.co.il/cards/board?link=https://farmaciait.men farmacie online sicure
Farmacie online sicure Farmacie online sicure and acquisto farmaci con ricetta acquisto farmaci con ricetta
farmacie online affidabili: BRUFEN 600 mg 30 compresse prezzo – acquistare farmaci senza ricetta
comprare farmaci online all’estero Farmacie online sicure acquistare farmaci senza ricetta
esiste il viagra generico in farmacia viagra senza ricetta pillole per erezione immediata
viagra subito pillole per erezioni fortissime or esiste il viagra generico in farmacia
https://maps.google.ml/url?q=https://sildenafilit.pro viagra originale in 24 ore contrassegno
viagra online spedizione gratuita viagra consegna in 24 ore pagamento alla consegna and viagra naturale in farmacia senza ricetta cerco viagra a buon prezzo
comprare farmaci online all’estero Cialis generico controindicazioni Farmacie online sicure
farmacie online sicure: Cialis generico 20 mg 8 compresse prezzo – farmaci senza ricetta elenco
pillole per erezione in farmacia senza ricetta viagra prezzo viagra prezzo farmacia 2023
farmacie online sicure Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita or <a href=" http://winkler-sandrini.it/info/mwst01i.pdf?a=places+to+buy+viagra+online “>farmacie online autorizzate elenco
https://maps.google.ms/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciait.men top farmacia online
acquisto farmaci con ricetta farmacia online piГ№ conveniente and Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita comprare farmaci online con ricetta
viagra online in 2 giorni: viagra generico sandoz – viagra ordine telefonico
viagra naturale in farmacia senza ricetta viagra generico esiste il viagra generico in farmacia
Farmacie online sicure: Farmacia online migliore – Farmacia online miglior prezzo
farmaci senza ricetta elenco BRUFEN 600 acquisto online top farmacia online
п»їFarmacia online migliore Ibuprofene 600 prezzo senza ricetta Farmacie online sicure
viagra ordine telefonico: viagra senza prescrizione – cialis farmacia senza ricetta
pillole per erezione in farmacia senza ricetta viagra online in 2 giorni or viagra online spedizione gratuita
http://devicedoctor.com/driver-feedback.php?device=PCI bus&url=https://sildenafilit.pro viagra 50 mg prezzo in farmacia
viagra naturale in farmacia senza ricetta miglior sito per comprare viagra online and pillole per erezione immediata pillole per erezioni fortissime
farmacia online senza ricetta: Brufen 600 prezzo con ricetta – п»їFarmacia online migliore
farmacia online senza ricetta Brufen 600 prezzo п»їFarmacia online migliore
Farmacia online miglior prezzo Cialis generico controindicazioni Farmacie online sicure
kamagra senza ricetta in farmacia: viagra online siti sicuri – viagra naturale
farmacia online piГ№ conveniente farmacia online piГ№ conveniente or comprare farmaci online all’estero
https://cse.google.be/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciait.men farmacia online
Farmacie online sicure acquisto farmaci con ricetta and top farmacia online farmaci senza ricetta elenco
ventolin online nz: Buy Albuterol for nebulizer online – ventolin tablet 2 mg
prednisone 250 mg: buy prednisone 1 mg mexico – cost of prednisone tablets
medicine neurontin: neurontin 800 mg tablet – generic neurontin cost
ventolin from mexico to usa: ventolin india – ventolin 4mg uk
neurontin 100mg tab neurontin cost generic or buy neurontin
http://toolbarqueries.google.nl/url?q=https://gabapentin.site neurontin for sale
medication neurontin 300 mg cost of neurontin 600 mg and neurontin 100mg tab neurontin 100mg tab
buy rybelsus: rybelsus – rybelsus generic
Rybelsus 7mg: Buy compounded semaglutide online – cheap Rybelsus 14 mg
order neurontin online neurontin 2400 mg or neurontin cost uk
http://www.1491.com.tw/phpinfo.php?a= how to get neurontin
neurontin 300 mg cap can you buy neurontin over the counter and gabapentin online neurontin tablets no script
furosemide 40 mg: lasix 100 mg tablet – lasix 100 mg
Viagra sans ordonnance livraison 48h Sildenafil Viagra Viagra prix pharmacie paris
Viagra homme prix en pharmacie sans ordonnance Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance Viagra gГ©nГ©rique sans ordonnance en pharmacie
http://vgrsansordonnance.com/# Viagra gГ©nГ©rique sans ordonnance en pharmacie
Pharmacie Internationale en ligne: Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher – trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie
Pharmacie sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie
pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale: cialis sans ordonnance – Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable